Types of Liver Disease
Dr. Pham Hoang Trung
The main types of liver diseases are liver malfunction, hepatitis (liver inflammation), cirrhosis (liver failure), and liver cancer. With liver malfunction, we can develop itching or rashes after eating meat or seafood (shrimp, crab, fish, etc.). If we eat spicy (chili or black pepper for example), we can easily grow pimples. In those cases, blood tests can show indices of the liver such as SGPT, SGOT, GGPT... at an elevated or still normal level.
One of the main functions of the liver is to filter blood to neutralize toxins through the following process: When food enters the intestines, it will be absorbed into the mesentery (a thin layer formed on the surface of the intestines). The absorbed nutritious substances will then pass through the liver where they are filtered so that any bacteria, toxins or other substances that our body can be allergic to will be neutralized. After that, the filtered nutritious substances will be taken into the blood in order to nourish the organic cells. If the liver is too deficient to filter the allergy-causing substances, when they enter the blood, they can cause itching, pimples or rashes on the skin, sometimes even sores in or around the mouth. A weak liver can also fail to handle the complex transformations of hormones, which then can darken our skin.
Hepatitis, by contrast, can be caused by too much intake of medications that are harmful to the liver or by living in a polluted environment. However, hepatitis is mostly contracted through the penetration of some viruses into our body. There are three main hepatitis virus types: Type A, type B, and type C.
The type A virus is transmitted from person to person through food that contains it. The B and C types are found in an infected person’s blood, saliva, female vaginal discharge, or male semen. The type B virus is transmitted through blood transfusion, needle sharing, sexual contact, or from the mother to the baby during childbirth. This virus can also enter our body through broken or scratched skin. The main transmission path of the type C virus is through blood as a result of needle sharing or blood transfusion before 1992 (prior to this year blood bags contaminated with the type C virus were not discarded due to lack of such information).
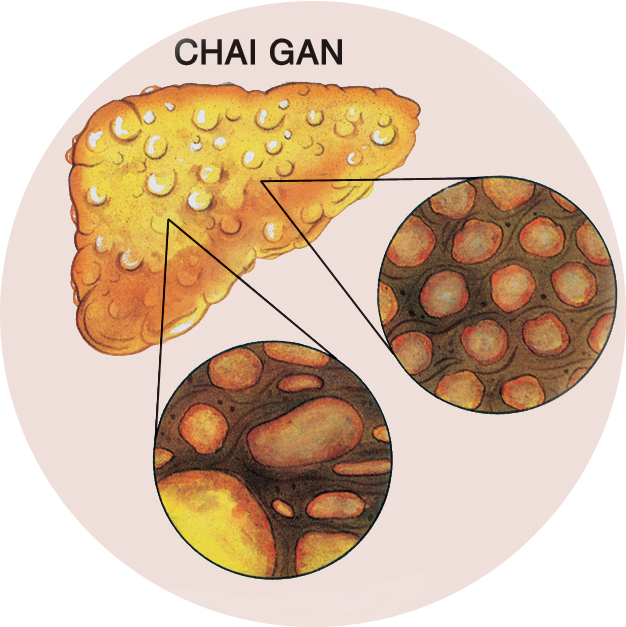 It is of more serious concern if we get hepatitis B or C hepatitis B or C since these two virus types have a potential to destroy the liver over a long period of time (chronic hepatitis). The C type virus is even more dangerous than the B type, for out of 70-80% of the cases, once having penetrated into the body, the C type will stay stubbornly there to continue attacking the liver (compared with only 5-10 % of the cases for the B type). If the virus stays in the liver for more than 6 months after penetration, it is considered to have caused chronic hepatitis.
It is of more serious concern if we get hepatitis B or C hepatitis B or C since these two virus types have a potential to destroy the liver over a long period of time (chronic hepatitis). The C type virus is even more dangerous than the B type, for out of 70-80% of the cases, once having penetrated into the body, the C type will stay stubbornly there to continue attacking the liver (compared with only 5-10 % of the cases for the B type). If the virus stays in the liver for more than 6 months after penetration, it is considered to have caused chronic hepatitis.
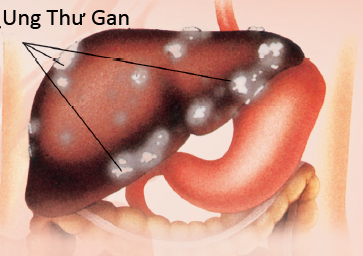
About 5-10% of chronic hepatitis B patients and 20% of chronic hepatitis C patients will slowly develop cirrhosis, by which liver tissues are gradually replaced by fiber tissues (within 10-20 years after the contraction of the hepatitis virus). Once cirrhosis has been developed, the chance of getting liver cancer (or hepato-cellular cancer) becomes very high. Liver cancer caused by cirrhosis is found in 75-95% of all the cases. A patient can only live up to an average of 6 months after the outbreak of the liver cancer symptoms.
Even though Hepatitis C is far more dangerous between the two types (causing chronic hepatitis and liver cancer more easily), the number of Hepatitis C patients is much less than that of Hepatitis B. Therefore, of all the reasons for liver cancer, Hepatitis B is still the leading one. According to surveys and researches, there can be up to 30-40% of all the Vietnamese living in the U.S. who have hepatitis and mostly it is Hepatitis B. The number of hepatitis patients living in Vietnam is even higher due to lack of sanitation and common knowledge of medicine.
Following is a brief discussion of the rarer hepatitis types, namely D, E, and G. The D type virus can exist and reproduce in the body only with the presence of the B type virus. If a patient is found to have the type B virus, followed by the presence of the D type virus, his hepatitis will be aggravated faster. Hepatitis E, on the other hand, is no more serious than Hepatitis A, so it is not something to worry too much about. Finally, Hepatitis G virus normally accompanies the A, B and C types, but this combination doesn’t aggravate the existing hepatitis.
If blood tests done to detect hepatitis indicate an increase of liver enzymes such as SGPT, SGOT, GGPT, etc., it is a sign that liver cells are being destroyed. At the same time, there appear in the blood antibodies and antigens of the contracted virus (B or C). (Antigens are substances secreted by viruses or bacteria to do harm to the body, whereas antibodies are molecules born by the immune system of the body to fight against the antigens).
 Hepatitis can easily advance to more serious stages if it is accompanied by unfavorable factors like drinking, using medications with side effects harmful to the liver, or the weakening of the immune system (a “defense” system that fights against viruses, bacteria or foreign substances penetrating into the body).
Hepatitis can easily advance to more serious stages if it is accompanied by unfavorable factors like drinking, using medications with side effects harmful to the liver, or the weakening of the immune system (a “defense” system that fights against viruses, bacteria or foreign substances penetrating into the body).
Under normal circumstances, the liver usually has a great endurance if attacked by viruses because it is capable of regenerate itself where it is damaged by the viruses. Nevertheless, if the attacks by the viruses continue as in the case of hepatitis, compounded by the above-mentioned unfavorable factors, the liver cells will not be able to regenerate indefinitely. The damaged cells will then leave behind scars in the liver, which leads to what we call cirrhosis (the liver gradually becoming hardened).
For that reason, aside from avoiding heavy drinking or overusing medications harmful to the liver, a hepatitis patient should also try to strengthen his immune system to effectively fight against the viruses and at the same time invigorate the liver cells to reinforce the ability of regenerating the cells damaged by the viruses.
Ghi chú thêm:
* People infected with hepatits (B or C) when taking blood test, should ask your doctor to test the followings:
- AST (SGOT), ALT (SGPT). These are liver enzymes. Average normal level is under 45
- If infected with hepatitis B, test the additional items:
- Hepatitis B Virus Antibodies
- Hepatitis B Surface Antigen
- Hepatitis B Virus DNA (amount of Hepatitis B virus in blood)
- If infected with hepatitis C, test the additional items:
- Hepatitis C Virus Antibodies
- Hepatitis C Virus RNA (amount of hepatitis C virus in blood)
DR. PHẠM HOANG TRUNG
9822 Bolsa Ave. Suite E – Westminster, CA 92683 – USA